Overview
The article provides insights into the relationship between alcohol consumption and GLP-1 medications, particularly for perimenopausal women. It highlights that GLP-1 treatments possess the feature of significantly reducing cravings and consumption of alcohol. This advantage aids in weight management, ultimately benefiting those seeking to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Furthermore, the article emphasizes the importance of consulting healthcare providers to navigate potential health risks associated with combining alcohol and these medications.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of weight management during perimenopause presents unique challenges for women, particularly regarding the interaction between alcohol consumption and GLP-1 medications. These treatments are increasingly recognized for their potential to reduce cravings and facilitate sustainable weight loss. Consequently, comprehending their impact on alcohol intake is essential.
How do these medications affect drinking behaviors, and what risks should women consider while striving for their health goals? This article explores seven key insights that clarify the relationship between alcohol and GLP-1, providing valuable guidance for women aiming to enhance their wellness journey.
Tyde Wellness: Personalized Weight Loss Programs with GLP-1 Medications
Tyde Wellness offers customized weight loss programs designed specifically for women, incorporating targeted treatments. These programs emphasize sustainable weight loss through a blend of medical expertise and personalized nutrition plans. By addressing the unique challenges that women face, particularly during perimenopause and menopause, Tyde Wellness empowers clients to achieve lasting results without the pitfalls of fad diets. Furthermore, the inclusion of specific medications assists in appetite management and enhances metabolic health, making the reduction of excess weight more achievable and sustainable.
GLP-1 Medications: Reducing Alcohol Cravings and Consumption
These treatments possess a significant ability to reduce cravings for beverages, including alcohol and GLP-1, positioning them as a practical option for individuals aiming to manage both body weight and beverage consumption. Research indicates that these medications can effectively diminish the desire for beverages, which is particularly beneficial for women experiencing hormonal fluctuations during perimenopause.
By addressing the intertwined challenges of body management and beverage cravings, therapies related to alcohol and GLP-1 foster a comprehensive approach to health and wellness. Notably, a study involving participants prescribed semaglutide or liraglutide for weight loss revealed that some individuals reported a decrease in consumption of alcohol and GLP-1 beverages of up to 68% within just four months.
Furthermore, a systematic review investigating the impact of GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) on alcohol and GLP-1 consumption suggests that while many participants experienced significant reductions in their intake of alcohol, the results from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have shown varied outcomes.
This dual focus not only aids in achieving weight loss goals but also enhances overall well-being, rendering these treatments a valuable resource in the pursuit of sustainable health transformations.
Health Risks: Alcohol Interaction with GLP-1 Medications
The combination of spirits and certain medications can pose significant health risks, particularly hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and digestive complications. Alcohol and GLP-1 have the potential to enhance the blood-sugar-lowering effects of specific treatments, which may lead to dangerously low blood sugar levels. Research indicates that individuals using certain medications may experience increased instances of hypoglycemia when consuming alcohol and GLP-1, necessitating careful monitoring of glucose levels. Additionally, both ethanol-containing drinks and certain medications can irritate the stomach lining, heightening the risk of nausea and other gastrointestinal discomforts.
Healthcare professionals emphasize the importance of recognizing these risks and recommend moderation in alcohol and GLP-1 consumption, which is defined as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to discuss safe drinking practices during weight loss therapy, as this proactive approach is vital for maintaining health and safety throughout the weight loss journey. Furthermore, recent studies suggest that certain medications may help reduce cravings and consumption of alcoholic beverages, providing a more balanced perspective on the relationship between these substances and weight loss therapy.
Emerging Research: GLP-1 Medications in Treating Alcohol Use Disorders
Recent research indicates that semaglutide may significantly assist in addressing issues related to substance use disorders (AUD), particularly when considering the effects of alcohol and GLP-1. These treatments have been shown to decrease both beverage intake and cravings for alcohol and GLP-1, offering a promising new strategy for those grappling with substance dependence.
Notably, a study involving 262 adults receiving specific therapies revealed that heavy drinkers reduced their alcohol and GLP-1 consumption by nearly 70% after starting treatment, with participants losing an average of 17 pounds over four months. Additionally, individuals in the semaglutide group experienced an average body mass loss of 5%, underscoring the effectiveness of these treatments in body management.
However, it is essential to recognize that despite these reductions, both semaglutide and placebo groups reported similar numbers of drinks per calendar day and drinking days throughout the study, which indicates some limitations in the treatment’s overall effectiveness regarding alcohol and GLP-1.
This emerging evidence underscores the adaptability of certain medications, suggesting they can effectively support recovery from substance use disorders related to alcohol and GLP-1 while also aiding in body mass management. This is particularly relevant for women undergoing hormonal changes during perimenopause, who often face unique challenges related to both weight and beverage intake.
Experts emphasize the potential of this therapy to provide a dual advantage, making it a valuable resource in the recovery toolkit for women navigating these life transitions.
Consult Healthcare Providers: Alcohol Guidelines for GLP-1 Users
Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals is essential for individuals using GLP-1 treatments in relation to alcohol and GLP-1 consumption. These experts offer tailored recommendations that consider each person’s health circumstances, treatment plans, and lifestyle factors. By assessing individual situations, healthcare providers help establish safe limits for beverage intake, allowing patients to participate in social settings without jeopardizing their health or weight loss objectives.
Notably, research has shown that adults taking medications like liraglutide or semaglutide have significantly reduced their alcohol and GLP-1 intake, with regular drinkers cutting back by 68% within four months of starting treatment. Additionally, the relationship between alcohol and GLP-1s may help decrease cravings for alcoholic beverages, underscoring the importance of open communication with healthcare providers. This dialogue is vital for effectively managing the complexities of alcohol consumption while undergoing hormone therapy.
Safe Practices: Enjoying Alcohol While on GLP-1 Medications
For women using weight-loss drugs, moderation in the consumption of alcohol and GLP-1 is essential for maintaining health and maximizing the benefits of their treatment. Here are some safe practices to consider:
- Limit intake to moderate levels—generally, up to one drink per day for women, as exceeding this can lead to negative health effects. Research indicates that participants on semaglutide reported consuming fewer drinks per drinking day, which suggests a connection between alcohol and GLP-1, as they experienced greater reductions in heavy drinking days over time.
- Stay hydrated by drinking water alongside alcoholic beverages to help mitigate potential side effects and support overall well-being.
- Avoid binge drinking, as the combination of alcohol and GLP-1 medications can exacerbate side effects and hinder weight loss efforts. Participants in weight loss programs have reported an average body weight reduction of 15% after 68 weeks, underscoring the importance of maintaining healthy habits.
- Monitor blood sugar levels closely, especially if consuming beverages on an empty stomach, as this can lead to fluctuations that may affect overall health.
- Always consult with a healthcare provider before making any changes to beverage consumption habits while on weight management therapy to ensure safety and effectiveness in achieving health goals. As noted by nutritionists, moderation is key to enjoying social occasions without compromising health.
By following these guidelines, women can partake in social events while prioritizing their health and wellness journey.
Implications: Understanding Alcohol and GLP-1 Medication Interactions
Understanding the interactions between spirits and specific treatments is essential for women, particularly those experiencing hormonal changes during perimenopause. GLP-1 treatments are designed not only to assist with weight management but also to significantly reduce cravings for alcohol and GLP-1. For example, a study indicated that heavy drinkers on semaglutide decreased their alcohol and GLP-1 beverage intake by nearly 70%.
However, it is crucial to assess the health risks associated with beverage consumption during this transitional phase, including an increased risk of certain cancers and potential interactions with medications. Women should maintain open communication with healthcare providers regarding their beverage consumption and adhere to safe drinking practices.
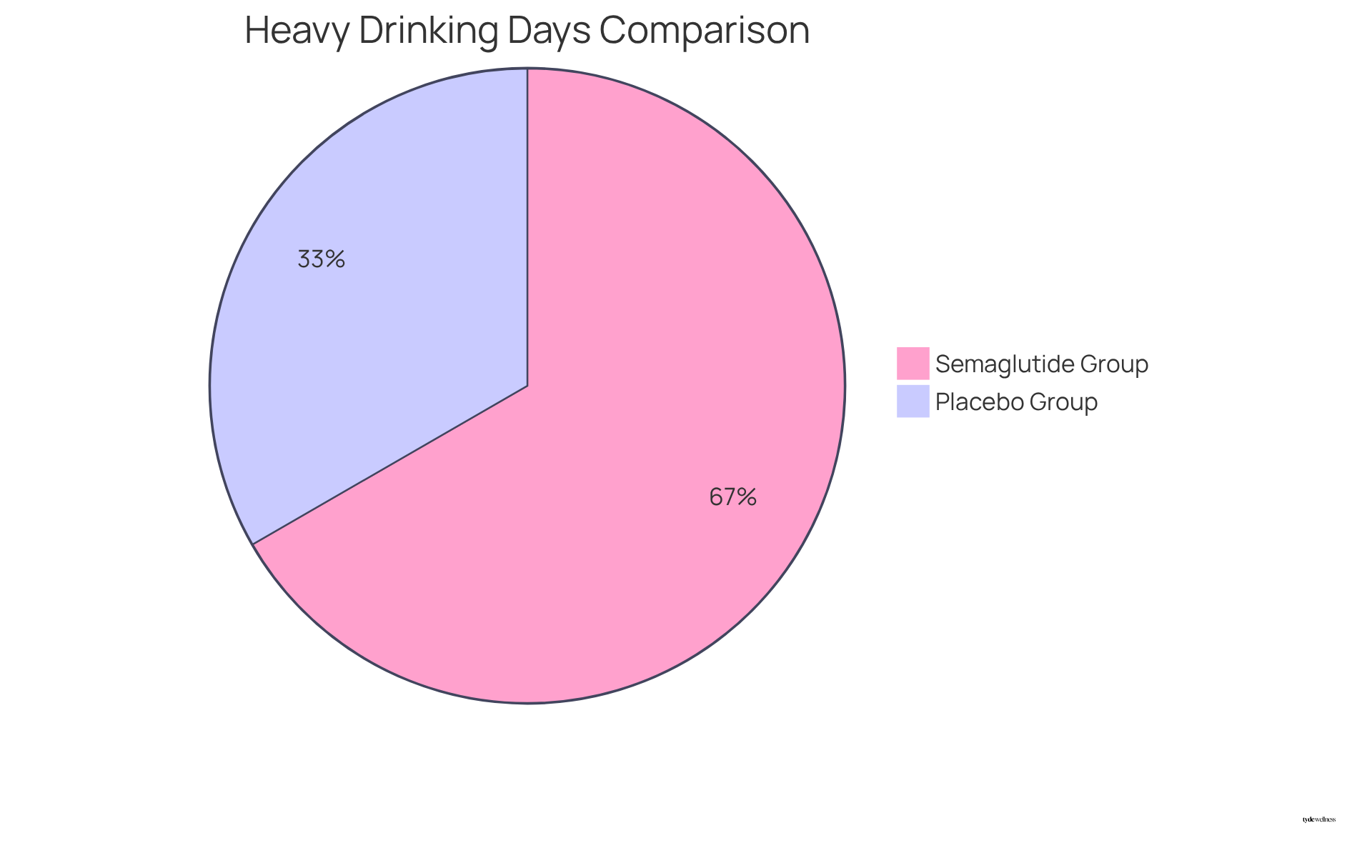
Notably, statistics reveal that approximately 40% of patients taking semaglutide reported no heavy drinking days, compared to just 20% in the placebo group, highlighting the potential benefits of this therapy in relation to alcohol and GLP-1. As Dr. Maurice O’Farrell observed, ‘They reduce dopamine release in reward pathways, which are common to food satisfaction but also to the pleasure people derive from beverages, such as alcohol and GLP-1.’
Staying informed about the latest research on GLP-1 medications and their effects on substance use empowers women to make informed choices that support their overall health and wellness. By understanding these dynamics, women can navigate their loss journeys more effectively while prioritizing their well-being. A practical takeaway is to regularly discuss any alcohol and GLP-1 consumption with healthcare providers to ensure a safe and effective weight loss journey.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between alcohol consumption and GLP-1 medications is crucial, especially for women navigating perimenopause. These treatments not only support weight management but also play a significant role in reducing cravings for alcohol. The insights presented highlight how GLP-1 medications can empower women to address both their weight loss goals and their beverage consumption in a balanced manner.
Key findings indicate that GLP-1 medications can lead to substantial reductions in alcohol intake, with studies showing participants decreasing their consumption by nearly 70% within months of treatment. Furthermore, the potential health risks associated with combining alcohol and GLP-1 medications, such as hypoglycemia and digestive issues, underscore the importance of moderation and professional guidance. Consulting with healthcare providers is essential to establish safe drinking practices and navigate the complexities of alcohol consumption during weight loss therapy.
Ultimately, staying informed about the effects of GLP-1 medications on alcohol use can significantly enhance the health and wellness journey for perimenopausal women. By fostering open communication with healthcare professionals and adhering to recommended guidelines, individuals can enjoy social occasions while prioritizing their health. Embracing this knowledge empowers women to make informed choices, ensuring a successful and sustainable approach to weight management and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Tyde Wellness and what do they offer?
Tyde Wellness offers personalized weight loss programs specifically designed for women, focusing on sustainable weight loss through medical expertise and tailored nutrition plans.
How does Tyde Wellness address the unique challenges faced by women?
Tyde Wellness addresses challenges particularly related to perimenopause and menopause, empowering clients to achieve lasting weight loss results without resorting to fad diets.
What role do GLP-1 medications play in Tyde Wellness programs?
GLP-1 medications assist in appetite management and enhance metabolic health, making it easier for clients to reduce excess weight sustainably.
How do GLP-1 medications help with alcohol cravings?
GLP-1 medications have been shown to significantly reduce cravings for beverages, including alcohol, making them a practical option for individuals looking to manage both body weight and beverage consumption.
What evidence supports the effectiveness of GLP-1 medications in reducing alcohol consumption?
Research indicates that participants prescribed semaglutide or liraglutide for weight loss reported a decrease in alcohol consumption of up to 68% within four months.
Are the results of GLP-1 medications consistent across all studies?
While many participants have experienced significant reductions in alcohol intake, results from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have shown varied outcomes.
How do GLP-1 medications contribute to overall health and wellness?
By addressing both weight loss goals and beverage cravings, GLP-1 therapies foster a comprehensive approach to health and wellness, aiding in sustainable health transformations.
List of Sources
- Tyde Wellness: Personalized Weight Loss Programs with GLP-1 Medications
- Advice for trying GLP-1 drugs for weight loss from a doctor who’s been there (https://npr.org/2025/06/15/nx-s1-5432864/weight-loss-drugs-glp1-wegovy-mounjaro)
- Women turn to weight loss drugs in menopause: What to know about the benefits and risks (https://abcnews.go.com/GMA/Wellness/women-turn-weight-loss-drugs-menopause-benefits-risks/story?id=115067358)
- A new era of weight loss: Mental health effects of GLP-1 drugs (https://apa.org/monitor/2025/07-08/weight-loss-drugs-mental-health)
- The Implications of GLP-1s on Women’s Healthcare (https://medscape.com/viewarticle/implications-glp-1s-womens-healthcare-2025a10009uh)
- GLP-1 Medications: Reducing Alcohol Cravings and Consumption
- Semaglutide Shows Promise in Reducing Cravings for Alcohol, Heavy Drinking | Newsroom (https://news.unchealthcare.org/2025/02/semaglutide-shows-promise-in-reducing-cravings-for-alcohol-heavy-drinking)
- GLP-1 Weight Loss Drugs Cut Alcohol Cravings By Two-Thirds (https://usnews.com/news/health-news/articles/2025-05-13/glp-1-weight-loss-drugs-cut-alcohol-cravings-by-two-thirds)
- Are GLP-1 Drugs the Future of Alcohol Addiction Treatment? (https://news-medical.net/health/Are-GLP-1-Drugs-the-Future-of-Alcohol-Addiction-Treatment.aspx)
- Ozempic shows some promise for alcohol use disorder (https://reuters.com/business/healthcare-pharmaceuticals/ozempic-shows-some-promise-alcohol-use-disorder-2025-02-12)
- Weight loss drug semaglutide may reduce alcohol cravings, heavy drinking and smoking, new study finds (https://abcnews.go.com/Health/weight-loss-drug-semaglutide-reduce-alcohol-cravings-heavy/story?id=118700712)
- Health Risks: Alcohol Interaction with GLP-1 Medications
- Study identifies benefits, risks linked to popular weight-loss drugs | WashU Medicine (https://medicine.washu.edu/news/study-identifies-benefits-risks-linked-to-popular-weight-loss-drugs)
- Can You Drink Alcohol While Taking GLP-1 Medications? Ozembic (https://healthyliferecovery.com/can-you-drink-alcohol-while-taking-glp-1-medications)
- Obesity drugs: huge study identifies new health risks (https://nature.com/articles/d41586-025-00173-5)
- Do GLP-1 drugs have health risks beyond their weight loss benefits? (https://medicalnewstoday.com/articles/glp-1-drugs-linked-lower-dementia-risk-higher-risk-kidney-stomach-issues)
- Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults With Alcohol Use Disorder (https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/fullarticle/2829811)
- Emerging Research: GLP-1 Medications in Treating Alcohol Use Disorders
- Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults With Alcohol Use Disorder (https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/fullarticle/2829811)
- Five things to know about GLP-1s and addiction (https://med.stanford.edu/news/insights/2025/04/ozempic-addiction-glp-1s-mounjaro-lembke.html)
- Weight-loss meds may give people more control over drinking, study shows (https://abcnews.go.com/GMA/Wellness/weight-loss-meds-give-people-control-drinking-study/story?id=121641974)
- GLP-1 medications: The next big thing in alcohol use disorder treatment? (https://recoveryanswers.org/research-post/glp-1-medications-next-big-thing-alcohol-use-disorder-treatment)
- Consult Healthcare Providers: Alcohol Guidelines for GLP-1 Users
- GLP-1 Weight Loss Drugs Cut Alcohol Cravings By Two-Thirds (https://usnews.com/news/health-news/articles/2025-05-13/glp-1-weight-loss-drugs-cut-alcohol-cravings-by-two-thirds)
- Are GLP-1 Drugs the Future of Alcohol Addiction Treatment? (https://news-medical.net/health/Are-GLP-1-Drugs-the-Future-of-Alcohol-Addiction-Treatment.aspx)
- GLP-1s tied to lower alcohol intake for adults with overweight, obesity (https://healio.com/news/endocrinology/20250512/glp1s-tied-to-lower-alcohol-intake-for-adults-with-overweight-obesity)
- Semaglutide and Tirzepatide reduce alcohol consumption in individuals with obesity – Scientific Reports (https://nature.com/articles/s41598-023-48267-2)
- Safe Practices: Enjoying Alcohol While on GLP-1 Medications
- Are GLP-1 Drugs the Future of Alcohol Addiction Treatment? (https://news-medical.net/health/Are-GLP-1-Drugs-the-Future-of-Alcohol-Addiction-Treatment.aspx)
- Healthy Returns: Ozempic helps curb alcohol use in new study — and doctors are concerned about telehealth GLP-1s (https://cnbc.com/2025/02/19/healthy-returns-ozempic-helps-curb-alcohol-use-in-new-study.html)
- GLP-1 medications: The next big thing in alcohol use disorder treatment? (https://recoveryanswers.org/research-post/glp-1-medications-next-big-thing-alcohol-use-disorder-treatment)
- Weight-loss meds may give people more control over drinking, study shows (https://abcnews.go.com/GMA/Wellness/weight-loss-meds-give-people-control-drinking-study/story?id=121641974)
- Implications: Understanding Alcohol and GLP-1 Medication Interactions
- Weight-loss meds may give people more control over drinking, study shows (https://abcnews.go.com/GMA/Wellness/weight-loss-meds-give-people-control-drinking-study/story?id=121641974)
- Ozempic for addiction: How an elite rehab center is using GLP-1s to ‘obliterate’ all kinds of cravings (https://statnews.com/2025/07/14/glp1-drugs-addiction-treatment-rehab-center-uses-weight-loss-drugs-to-reduce-cravings)
- Study Shows Semaglutide Holds Promise in Reducing Alcohol Cravings (https://pharmacytimes.com/view/study-shows-semaglutide-holds-promise-in-reducing-alcohol-cravings)
- Are GLP-1 Drugs the Future of Alcohol Addiction Treatment? (https://news-medical.net/health/Are-GLP-1-Drugs-the-Future-of-Alcohol-Addiction-Treatment.aspx)
- GLP-1 Drug Semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy) Reduced Heavy Drinking & Craving in Adults with Alcohol Use Disorder | Brain & Behavior Research Foundation (https://bbrfoundation.org/content/glp-1-drug-semaglutide-ozempic-wegovy-reduced-heavy-drinking-craving-adults-alcohol-use)



