Overview
The primary distinction between progestin and progesterone lies in their origins: progestin is a synthetic derivative of progesterone, whereas progesterone is a naturally occurring hormone produced by the ovaries. This article emphasizes that these differences significantly affect their roles in women’s health, therapeutic applications, and associated risks. Notably, natural progesterone typically presents a more favorable safety profile compared to synthetic progestin, particularly regarding the risk of breast cancer.
Introduction
The intricate balance of hormones is pivotal to women’s health, yet the distinctions between progestin and progesterone often remain unclear. Understanding these differences is crucial, as they can significantly impact treatment choices and health outcomes.
- Progestin, a synthetic derivative, is widely used in contraceptives and hormone replacement therapies.
- In contrast, natural progesterone offers unique benefits and risks that warrant careful consideration.
How do these two hormones compare in terms of safety, effectiveness, and their roles in female physiology? This article delves into the essential contrasts between progestin and progesterone, empowering women to make informed decisions about their hormonal health.
Understanding Progestin and Progesterone: Definitions and Functions
When discussing progestin vs progesterone, it is important to note that progestin is a synthetic derivative of progesterone, designed to replicate its physiological effects within the body. In contrast, when exploring progestin vs progesterone, it is important to understand that progesterone is a naturally occurring substance produced by the ovaries, particularly during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle and throughout pregnancy. Both progestin vs progesterone play crucial roles in regulating the menstrual cycle, preparing the uterus for potential pregnancy, and maintaining pregnancy once it occurs.
Recent studies have highlighted the differing effects of hormones, specifically progestin vs progesterone, on female health, particularly in relation to hormonal therapies. For instance, while progestin vs progesterone shows that progestin is often used in combination treatments, research indicates it may carry risks, such as an increased likelihood of breast cancer compared to natural progesterone. Specifically, individuals undergoing combination estrogen-and-progestin therapy who experience new-onset breast tenderness face a 33% greater risk of developing breast cancer.
Furthermore, ongoing research suggests that hormonal treatment may offer benefits beyond alleviating hot flashes, including potential protection against bone loss and heart disease. Understanding the differences in progestin vs progesterone is essential for evaluating their individual roles in hormonal treatments and their broader implications for female health. It is also important for women to discuss treatment options with their healthcare providers to ensure personalized care.
Roles in Women’s Health: Progestin vs. Progesterone
Progesterone plays a crucial role in regulating the menstrual cycle and supporting pregnancy. Its primary function is to thicken the uterine lining, making it suitable for implantation. In contrast, the discussion of progestin vs progesterone reveals that progestin, which performs comparable roles, is frequently utilized in contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to address menopause symptoms.
The key difference between progestin vs progesterone lies in their origin:
- Progesterone is natural.
- Progestin is synthetic.
This distinction can significantly influence how each hormone interacts with the body and its overall effectiveness in treatment protocols.
Therapeutic Uses: Comparing Applications in Hormonal Treatments
Progesterone plays a crucial role in fertility treatments, particularly for individuals with a history of miscarriage. It supports pregnancy and helps manage irregular menstrual cycles and endometrial hyperplasia. A study involving 4,153 individuals randomized to receive either progesterone or placebo demonstrated its effectiveness in improving live birth rates among those experiencing early pregnancy complications. In contrast, this hormone is predominantly utilized in various contraceptive methods, including the progestin-only pill and hormonal IUDs, as well as in hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to alleviate menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes and night sweats, which illustrates the distinctions in progestin vs progesterone.
Recent data shows that this hormone is a popular option among individuals looking for effective contraceptive methods, with its uses growing in the past few years. Furthermore, the FDA initially authorized the Opill contraceptive pill in 1973, emphasizing the enduring application of this hormone in reproductive health. Understanding the distinct uses of progestin vs progesterone empowers women to make informed decisions about their hormonal health and reproductive choices.
Side Effects and Risks: Evaluating Safety Profiles
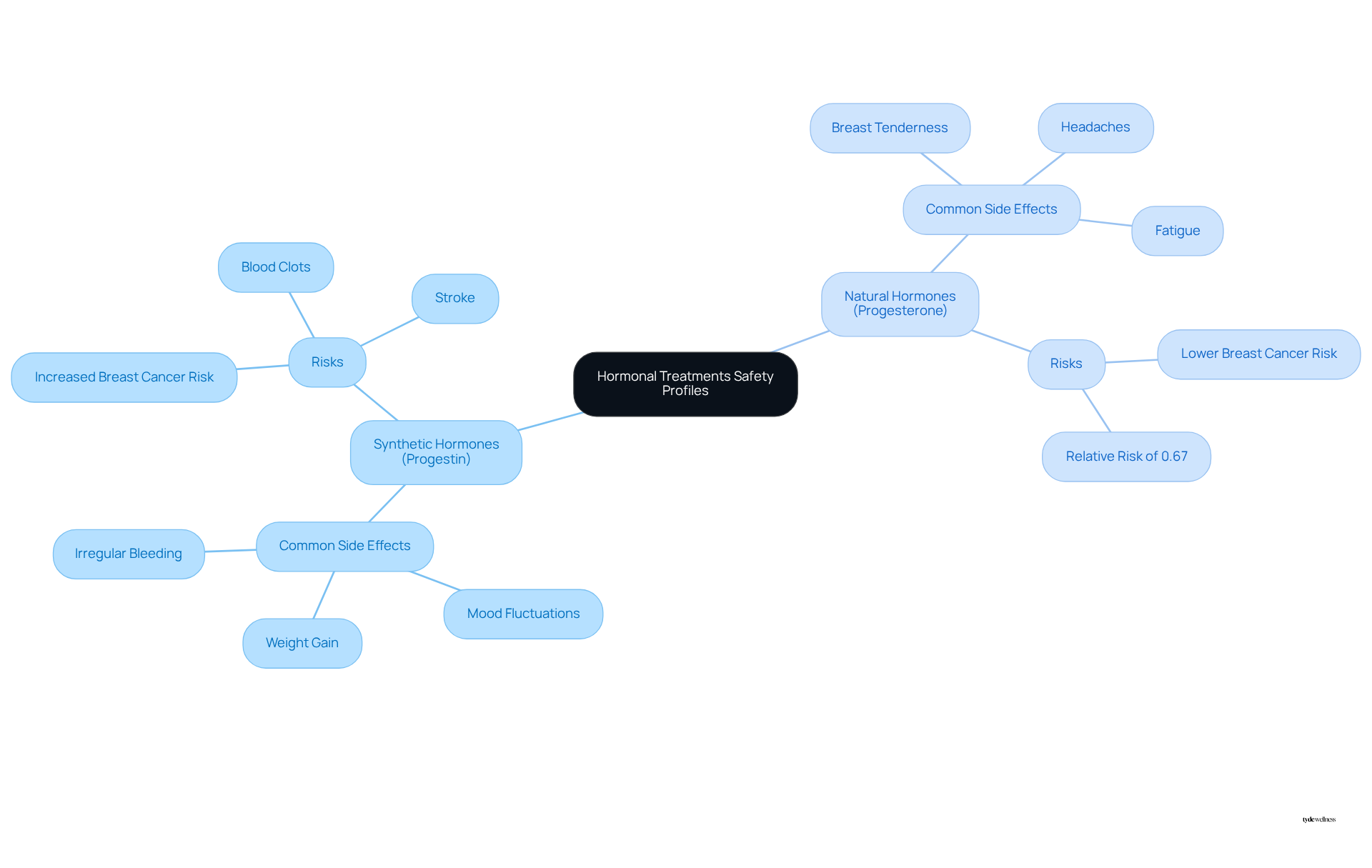
When considering progestin vs progesterone, both can lead to side effects, yet their safety profiles exhibit notable differences. Common side effects linked to synthetic hormones include:
- Weight gain
- Mood fluctuations
- Irregular bleeding
In contrast, natural progesterone may result in:
- Breast tenderness
- Fatigue
- Headaches
Significantly, synthetic hormones have been associated with an increased risk of severe health problems, including blood clots and breast cancer, particularly with prolonged use. Studies indicate that females utilizing estrogen combined with progestin vs progesterone treatment (EP-HT) encounter a 10% greater rate of breast cancer compared to non-users, with individuals on EP-HT for more than two years facing an 18% heightened risk. Conversely, when considering progestin vs progesterone, natural progesterone has been associated with a lower breast cancer risk, with a relative risk of 0.67 when combined with estrogen. Furthermore, females utilizing unopposed estrogen medication (E-HT) experienced a 14% decrease in breast cancer occurrence compared to those who have never utilized such treatment.
The FDA’s boxed warning on estrogen treatments highlights that they increase the risk of stroke, deep vein thrombosis, and dementia, further emphasizing the safety concerns surrounding hormonal treatments. Historical context is also crucial; the Women’s Health Initiative study from 2002 led many healthcare providers to discontinue prescribing hormone therapy due to increased risks of invasive breast cancer, pulmonary embolism, and stroke. Understanding these risks is essential for women contemplating hormonal treatments, particularly during menopause, as it empowers them to make informed decisions regarding their health.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between progestin and progesterone is crucial for women’s health, as these hormones significantly impact reproductive and overall well-being. Progesterone is a natural hormone produced by the ovaries, while progestin is a synthetic derivative designed to mimic its effects. This fundamental difference influences their applications in hormonal treatments, efficacy, and associated health risks.
The article highlights several key points, including:
- The therapeutic uses of both hormones
- Their roles in regulating the menstrual cycle
- Their distinct safety profiles
Natural progesterone is often favored due to its lower associated risks, particularly concerning breast cancer, compared to synthetic progestin. Furthermore, understanding the side effects linked to each hormone empowers women to make informed decisions about their health and treatment options.
Ultimately, recognizing the differences between progestin and progesterone is of paramount importance. Women are encouraged to engage in open discussions with healthcare providers to explore personalized approaches to hormonal health. By prioritizing informed choices, individuals can better navigate their health journeys, ensuring they select the most appropriate and safe treatments for their unique needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between progestin and progesterone?
Progestin is a synthetic derivative of progesterone, designed to replicate its physiological effects, while progesterone is a naturally occurring hormone produced by the ovaries during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle and throughout pregnancy.
What roles do progestin and progesterone play in the body?
Both progestin and progesterone play crucial roles in regulating the menstrual cycle, preparing the uterus for potential pregnancy, and maintaining pregnancy once it occurs.
What are the risks associated with progestin compared to natural progesterone?
Research indicates that progestin may carry risks such as an increased likelihood of breast cancer compared to natural progesterone, particularly in individuals undergoing combination estrogen-and-progestin therapy.
How does progestin affect breast cancer risk?
Individuals undergoing combination estrogen-and-progestin therapy who experience new-onset breast tenderness have a 33% greater risk of developing breast cancer.
What potential benefits might hormonal treatments provide beyond alleviating hot flashes?
Ongoing research suggests that hormonal treatments may offer benefits such as protection against bone loss and heart disease.
Why is it important for women to understand the differences between progestin and progesterone?
Understanding the differences is essential for evaluating their individual roles in hormonal treatments and their broader implications for female health, allowing for informed discussions with healthcare providers about treatment options.
List of Sources
- Understanding Progestin and Progesterone: Definitions and Functions
- Progesterone Research Explores New Pathways to Treat Cancer | The University of Kansas Cancer Center (https://kucancercenter.org/research/transformative-research/beyond-the-bench/2024/progesterone-research-explores-new-pathways-to-treat-cancer)
- Hormones for menopause are safe, study finds. Here’s what changed (https://npr.org/sections/health-shots/2024/05/01/1248525256/hormones-menopause-hormone-therapy-hot-flashes)
- Certain type of hormone therapy increases breast cancer risk, study finds (https://cbsnews.com/news/hormone-therapy-breast-cancer-risk-study)
- Breast tenderness during combination hormone therapy linked to higher cancer risk (https://uclahealth.org/news/release/hormone-therapy-linked-to-higher-cancer-risk)
- Contemporary menopausal hormone therapy and risk of cardiovascular disease: Swedish nationwide register based emulated target trial (https://bmj.com/content/387/bmj-2023-078784)
- Roles in Women’s Health: Progestin vs. Progesterone
- Menopause Hormone Therapy is Making a Comeback: Is it Safe and Right for You? | (https://longevity.stanford.edu/lifestyle/2025/03/06/menopause-hormone-therapy-is-making-a-comeback-is-it-safe-and-right-for-you)
- Black box warning on menopause hormone therapies should be removed, experts say | CNN (https://cnn.com/2025/07/24/health/menopause-hormone-treatment-wellness)
- Why Intravaginal Progesterone Therapy is a Smart Choice and a Smart Investment | Calla Lily Clinical Care (https://callali.ly/ko-kr/news/2025-01-14/why-intravaginal-progesterone-therapy-is-a-smart-choice-and-a-smart-investment)
- Breast cancer risk in younger women may be influenced by hormone therapy (https://nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/breast-cancer-risk-younger-women-may-be-influenced-hormone-therapy)
- Therapeutic Uses: Comparing Applications in Hormonal Treatments
- Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Researchers Secure Funding to Explore Progesterone Therapy Response Mechanisms in Fetuses with Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) (https://chop.edu/news/childrens-hospital-philadelphia-researchers-secure-funding-explore-progesterone-therapy)
- Giving some pregnant women progesterone could prevent 8,450 miscarriages a year, say experts (https://tommys.org/about-us/charity-news/giving-some-pregnant-women-progesterone-could-prevent-8450-miscarriages-year-say-experts)
- First over-the-counter birth control pill shipped in US (https://bbc.com/news/world-us-canada-66191585)
- Progesterone to prevent miscarriage in women with early pregnancy bleeding: the PRISM RCT – PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7355406)
- Side Effects and Risks: Evaluating Safety Profiles
- FDA commissioner stirs debate over hormone therapy for menopause (https://thehill.com/policy/healthcare/5412519-hormone-therapy-black-box-warning)
- Certain type of hormone therapy increases breast cancer risk, study finds (https://cbsnews.com/news/hormone-therapy-breast-cancer-risk-study)
- Breast cancer risk in younger women may be influenced by hormone therapy (https://nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/breast-cancer-risk-younger-women-may-be-influenced-hormone-therapy)
- Progesterone vs. synthetic progestins and the risk of breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis – Systematic Reviews (https://systematicreviewsjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13643-016-0294-5)
- Progesterone and Breast Cancer – PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7156851)



