Overview
Tirzepatide and Semaglutide present notable differences in their safety profiles and efficacy for weight loss in perimenopausal women.
- Tirzepatide is generally associated with greater body mass reduction; however, it is linked to higher gastrointestinal side effects.
- In contrast, Semaglutide may offer a safer alternative for individuals who are sensitive to side effects.
This distinction underscores the importance of personalized treatment plans when managing health during menopause, ensuring that each woman can choose the option that best aligns with her health needs and lifestyle.
Introduction
As the landscape of weight management evolves, perimenopausal women encounter distinct challenges that can complicate their health journeys. The introduction of medications such as Tirzepatide and Semaglutide necessitates a clear understanding of their unique mechanisms and safety profiles for informed decision-making. This article explores the comparative safety and efficacy of these two GLP-1 receptor agonists, raising critical questions about which option may be more suitable for women experiencing the hormonal fluctuations of perimenopause.
How do these medications compare in terms of weight loss outcomes and potential side effects? Furthermore, what considerations should women take into account when selecting the appropriate treatment for their needs?
Understanding Tirzepatide and Semaglutide: Mechanisms of Action
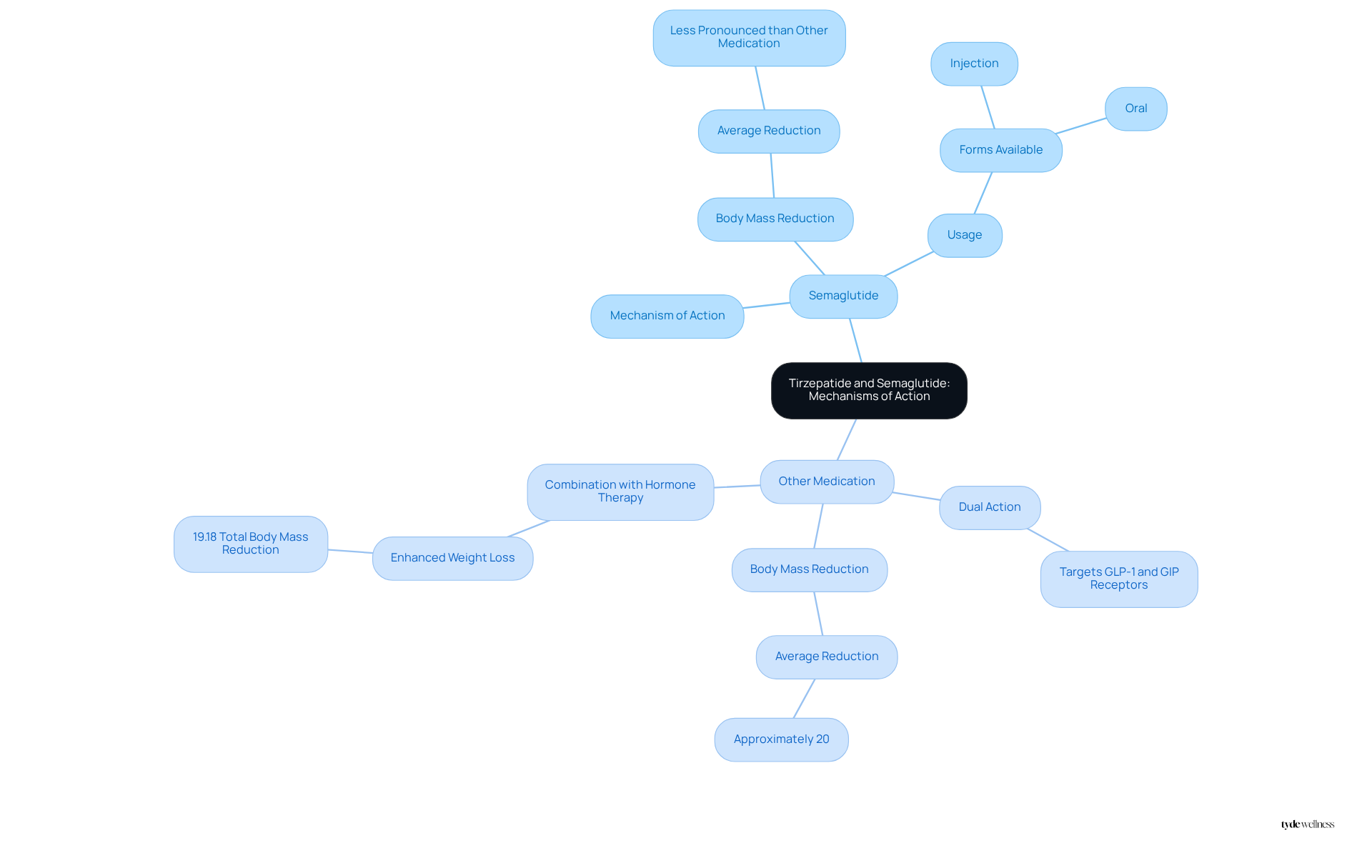
Semaglutide and another medication are both classified as GLP-1 receptor agonists, yet they exhibit notable differences in their mechanisms of action. The other medication functions as a dual agonist, targeting both GLP-1 and GIP receptors. This dual action enhances insulin release and significantly reduces appetite, potentially making it more effective for managing body mass compared to Semaglutide, which primarily activates GLP-1 receptors. The unique mechanism of this medication may offer additional benefits for metabolic health, particularly for individuals experiencing hormonal changes during perimenopause and menopause.
Both medications replicate the effects of incretin hormones released in response to food intake, promoting feelings of fullness and reducing caloric consumption. Clinical studies have demonstrated that this medication leads to a substantial reduction in body mass, with participants experiencing an average decrease of approximately 20% across various reproductive phases, including premenopausal, perimenopausal, and postmenopausal women. In contrast, while Semaglutide has also proven effective, its outcomes in body mass reduction are generally less pronounced than those associated with the other medication.
Research indicates that combining GLP-1 receptor agonists with menopausal hormone therapy can further enhance fat reduction results. For instance, a study revealed that postmenopausal individuals using a specific medication alongside hormone treatment achieved a 19.18% total body mass reduction, compared to 13.96% in those not receiving hormone therapy. This suggests that the treatment may be particularly beneficial for women navigating the challenges of . Furthermore, at Tyde Wellness, we offer optional peptide and hormonal therapies to further support you on your journey to achieving a healthier body. Our board-certified obesity medicine providers are committed to collaborating with you to develop a personalized plan that aligns with your goals. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to discuss potential risks associated with GLP-1 medications and to identify the most suitable treatment options, including the various forms of Semaglutide, which are available in both injection and oral formats.
Comparative Efficacy: Tirzepatide vs. Semaglutide in Weight Loss
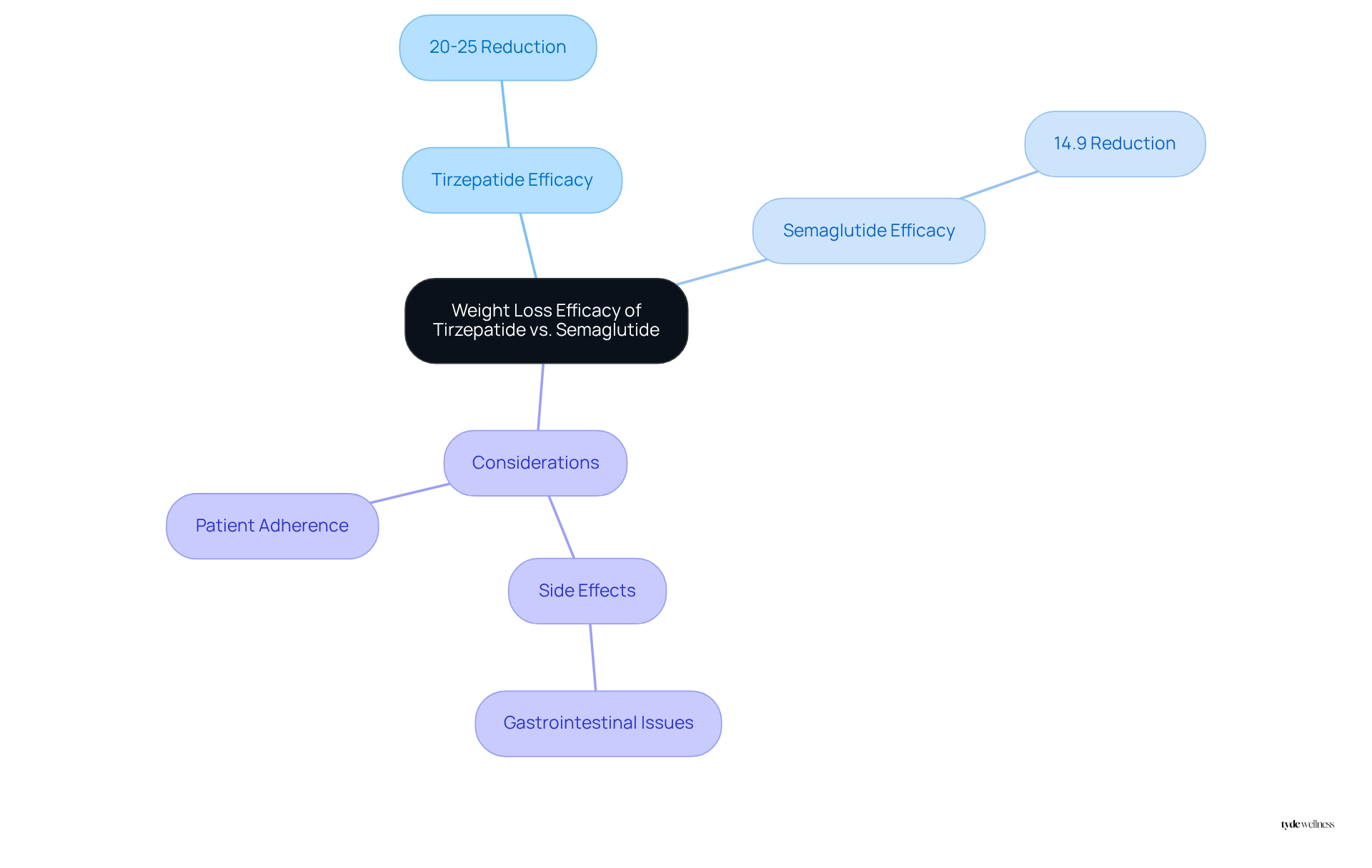
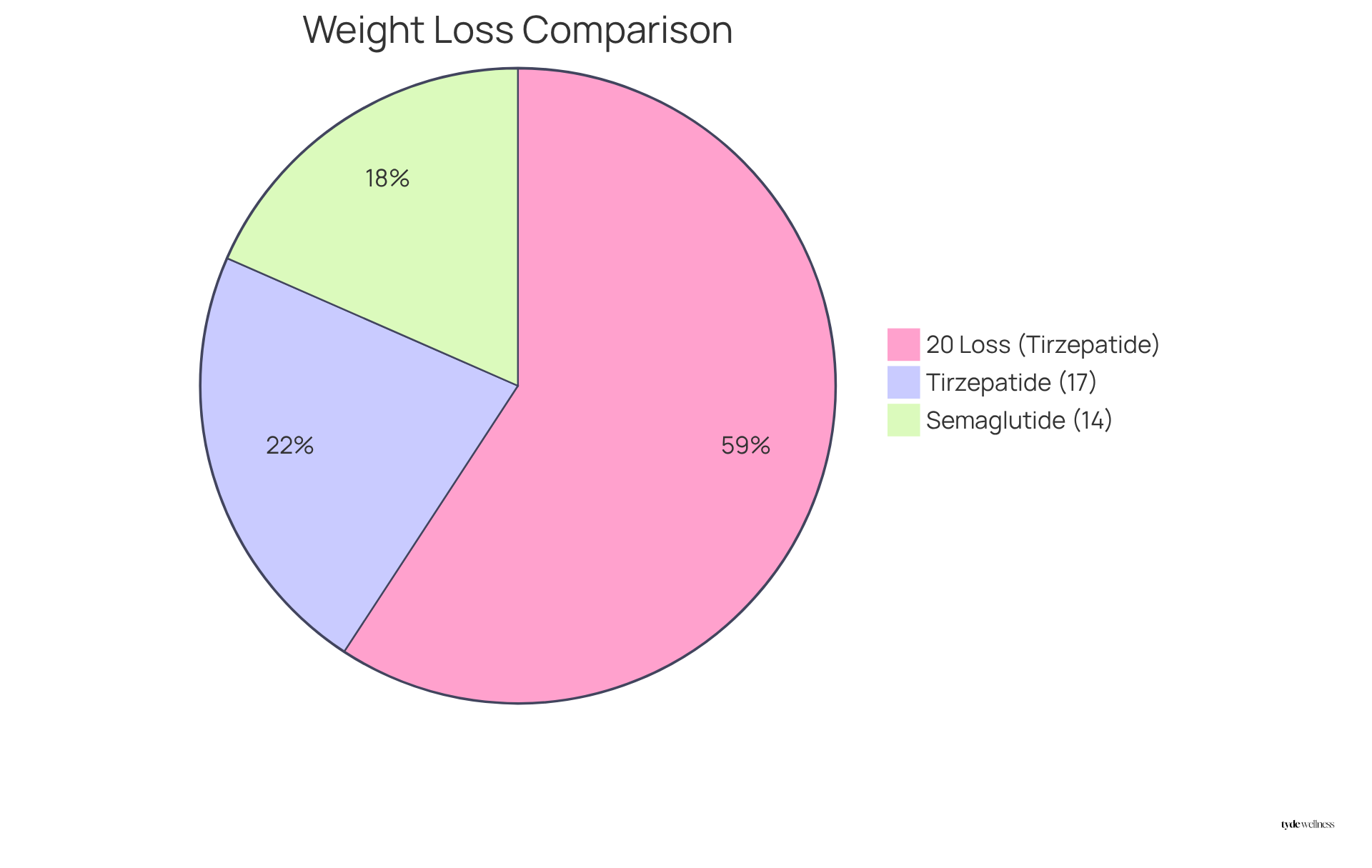
Clinical studies indicate that Tirzepatide typically results in a more substantial reduction in body mass compared to Semaglutide. Participants utilizing Tirzepatide have reported an average mass reduction of approximately 20-25% over the span of a year, whereas those on Semaglutide generally experience around a 14.9% loss after 68 weeks. This distinction holds particular significance for individuals in perimenopause, who often face due to hormonal fluctuations.
At Tyde Wellness, we recognize these unique challenges and provide a comprehensive approach that includes personalized peptide therapy and GLP-1 treatment programs tailored to each woman’s specific needs. The dual-action mechanism of Tirzepatide, which targets both glucose-dependent insulin secretion and appetite regulation, may enhance its efficacy, making it an appealing option for those seeking notable reductions in body mass.
Recent clinical trials, including a new head-to-head study, have further corroborated these findings, confirming that Tirzepatide leads to more significant reductions in body mass on average than Semaglutide. By integrating our supportive care model, which encompasses regular check-ins and expert guidance, we empower women to navigate the complexities of managing their health during pivotal life stages.
Additionally, it is essential to consider potential side effects, such as gastrointestinal issues, associated with both medications when evaluating Tirzepatide vs Semaglutide safety, as well as the importance of patient adherence to medication regimens in achieving desired weight loss outcomes.
Safety Profiles: Analyzing Risks and Side Effects of Tirzepatide and Semaglutide
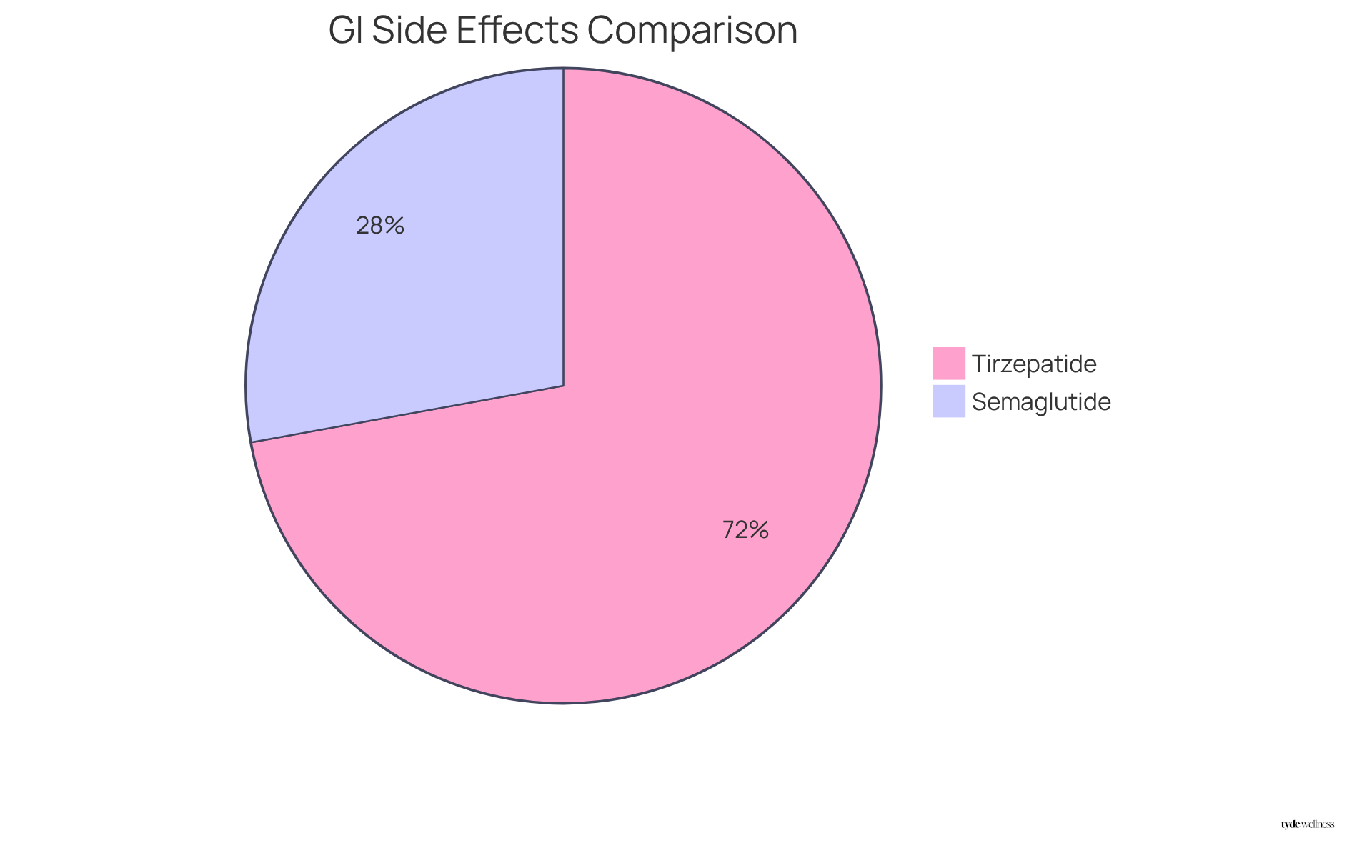
Semaglutide and another GLP-1 receptor agonist share similar side effects, primarily such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. However, evidence suggests that when considering tirzepatide vs semaglutide safety, tirzepatide is associated with a notably higher incidence of gastrointestinal adverse events, with approximately 79.8% of users experiencing these issues compared to 30.81% for semaglutide. This significant disparity highlights the importance of considering individual reactions, especially for those in perimenopause who may experience heightened sensitivity to these side effects due to hormonal fluctuations.
Additionally, there are concerns regarding the risk of pancreatitis and thyroid tumors linked to both medications, raising questions about tirzepatide vs semaglutide safety, although these occurrences remain rare. Given the potential for increased side effects in this demographic, it is essential for women to engage in regular monitoring and maintain open communication with healthcare providers to effectively manage any adverse effects. As noted by specialists in the field, tailored treatment strategies are vital to ensuring long-term success and safety in management therapies.
Suitability for Women: Choosing Between Tirzepatide and Semaglutide
When assessing the medication in comparison to Semaglutide, it is essential to consider personal health conditions, reduction goals, and the . This medication has shown promising results for individuals aiming for significant weight loss, particularly those undergoing hormone treatment for menopause. Research indicates that combining this medication with hormone therapy can lead to enhanced reductions in body mass. Studies reveal that women utilizing both treatments lost an average of 17% of their total body mass, compared to 14% for those on the medication alone. Notably, 45% of female patients receiving hormone treatment alongside this medication achieved at least a 20% total body weight reduction, highlighting its effectiveness in this demographic.
Conversely, individuals who prioritize a medication with a well-established safety profile and fewer gastrointestinal side effects may find Semaglutide more suitable when evaluating tirzepatide vs semaglutide safety. Semaglutide is recognized for its superior efficacy in reducing the risk of cardiovascular events, making it an attractive option for those concerned about heart health.
Ultimately, the choice regarding tirzepatide vs semaglutide safety should be made in consultation with healthcare providers, considering personal health histories and lifestyle factors. This personalized approach ensures that women can select the most appropriate treatment to support their weight loss journey during menopause.
Conclusion
The exploration of Tirzepatide and Semaglutide reveals crucial insights for perimenopausal women navigating weight management and hormonal changes. Both medications serve as GLP-1 receptor agonists; however, their mechanisms and efficacy differ significantly. Tirzepatide, with its dual-action targeting both GLP-1 and GIP receptors, offers a more pronounced effect on body mass reduction. This makes it a compelling option for those seeking substantial weight loss during this transitional phase of life.
Key arguments highlight that:
- Tirzepatide can lead to a body mass reduction of approximately 20-25%, significantly surpassing the 14.9% average loss associated with Semaglutide.
- The combination of GLP-1 medications with hormone therapy further enhances weight loss outcomes, particularly for women experiencing the challenges of menopause.
- It is vital to consider the safety profiles of these medications, as Tirzepatide has been linked to a higher incidence of gastrointestinal side effects compared to Semaglutide.
This underscores the importance of personalized treatment plans that take into account individual health conditions and preferences.
Ultimately, the decision between Tirzepatide and Semaglutide should involve careful consultation with healthcare providers to ensure the chosen medication aligns with personal health goals and safety considerations. By prioritizing informed choices and tailored approaches, perimenopausal women can effectively manage their health and achieve their weight loss objectives during this critical life stage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Semaglutide and the other medication mentioned in the article?
Semaglutide and the other medication are both classified as GLP-1 receptor agonists, but the other medication functions as a dual agonist, targeting both GLP-1 and GIP receptors.
How do the mechanisms of action differ between Semaglutide and the other medication?
The other medication enhances insulin release and significantly reduces appetite through its dual action on GLP-1 and GIP receptors, while Semaglutide primarily activates GLP-1 receptors.
What benefits does the dual action of the other medication provide?
The dual action may offer additional benefits for metabolic health, particularly for individuals experiencing hormonal changes during perimenopause and menopause.
How do these medications affect appetite and caloric consumption?
Both medications replicate the effects of incretin hormones released in response to food intake, promoting feelings of fullness and reducing caloric consumption.
What results have clinical studies shown regarding body mass reduction with the other medication?
Clinical studies have shown that the other medication can lead to an average body mass reduction of approximately 20% across various reproductive phases in women.
How does the body mass reduction outcome of Semaglutide compare to the other medication?
While Semaglutide is effective, its outcomes in body mass reduction are generally less pronounced compared to those associated with the other medication.
Can combining GLP-1 receptor agonists with menopausal hormone therapy enhance fat reduction?
Yes, research indicates that combining GLP-1 receptor agonists with menopausal hormone therapy can further enhance fat reduction results.
What were the results of the study comparing postmenopausal individuals using the other medication with and without hormone therapy?
The study revealed that those using the medication alongside hormone treatment achieved a 19.18% total body mass reduction, compared to 13.96% in those not receiving hormone therapy.
What services does Tyde Wellness offer to support individuals on their health journey?
Tyde Wellness offers optional peptide and hormonal therapies and collaborates with individuals to develop personalized plans aligned with their health goals.
Why is it important to consult with a healthcare provider regarding GLP-1 medications?
It is crucial to discuss potential risks associated with GLP-1 medications and to identify the most suitable treatment options, including the various forms of Semaglutide available.
List of Sources
- Understanding Tirzepatide and Semaglutide: Mechanisms of Action
- Study reveals distinct mechanisms of action of tirzepatide and semaglutide (https://eurekalert.org/news-releases/1083711)
- Menopausal hormone therapy may boost weight loss seen with Zepbound (https://healio.com/news/endocrinology/20250713/menopausal-hormone-therapy-may-boost-weight-loss-seen-with-zepbound)
- Tirzepatide Tops Semaglutide for Weight Loss: SURMOUNT-5 (https://tctmd.com/news/tirzepatide-tops-semaglutide-weight-loss-surmount-5)
- Women in Menopause Benefit From GLP-1 Weight-Loss Medications as Much as Younger Women | Research | Advances in Endocrinology, and Women’s Health | NewYork-Presbyterian (https://nyp.org/advances/article/women-in-menopause-benefit-from-glp-1-weight-loss-medications-as-much-as-younger-women)
- Menopause Weight Gain: Can GLP-1 Medications Help? (https://healthline.com/health/menopause/can-you-use-glp-1-medications-for-menopause-weight-gain)
- Comparative Efficacy: Tirzepatide vs. Semaglutide in Weight Loss
- Tirzepatide Outperforms Semaglutide in Head-to-Head Obesity Trial (https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2835190)
- Head-to-Head Trial Compares Weight Loss Drugs | Weill Department of Medicine (https://medicine.weill.cornell.edu/news/head-head-trial-compares-weight-loss-drugs)
- Semaglutide vs Tirzepatide for Weight Loss in Adults With Overweight or Obesity (https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2821080)
- Lilly’s Zepbound® (tirzepatide) superior to Wegovy® (semaglutide) in head-to-head trial showing an average weight loss of 20.2% vs. 13.7% | Eli Lilly and Company (https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lillys-zepboundr-tirzepatide-superior-wegovyr-semaglutide-head)
- Safety Profiles: Analyzing Risks and Side Effects of Tirzepatide and Semaglutide
- Tirzepatide bests semaglutide for weight loss in adults with obesity (https://healio.com/news/endocrinology/20250513/tirzepatide-bests-semaglutide-for-weight-loss-in-adults-with-obesity)
- Tirzepatide tops the charts for blood sugar and weight loss in type 2 diabetes (https://news-medical.net/news/20250707/Tirzepatide-tops-the-charts-for-blood-sugar-and-weight-loss-in-type-2-diabetes.aspx)
- Weighing up the Risks: GI Side Effects of Semaglutide vs Tirzepatide (https://emjreviews.com/gastroenterology/news/weighing-up-the-risks-gi-side-effects-of-semaglutide-vs-tirzepatide)
- Tirzepatide Tops Semaglutide for Weight Loss: SURMOUNT-5 (https://tctmd.com/news/tirzepatide-tops-semaglutide-weight-loss-surmount-5)
- Suitability for Women: Choosing Between Tirzepatide and Semaglutide
- Tirzepatide, Hormone Therapy Combination Increases Weight Loss in Postmenopausal Women (https://drugtopics.com/view/tirzepatide-hormone-therapy-combination-increases-weight-loss-among-postmenopausal-women)
- Combination of obesity medication tirzepatide and menopause hormone therapy fuels weight loss (https://endocrine.org/news-and-advocacy/news-room/endo-annual-meeting/endo-2025-press-releases/castaneda-press-release)
- Hormone Therapy Plus Tirzepatide Enhances Postmenopausal Weight Loss (https://thecardiologyadvisor.com/news/hormone-therapy-plus-tirzepatide-enhances-postmenopausal-weight-loss)
- Superior Weight Loss Seen With Tirzepatide and Menopausal Hormone Therapy Use (https://gastroenterologyadvisor.com/news/superior-weight-loss-seen-with-tirzepatide-and-menopausal-hormone-therapy-use)
- Hormone therapy supercharges tirzepatide, unleashing major weight loss after menopause (https://sciencedaily.com/releases/2025/07/250713031441.htm)



